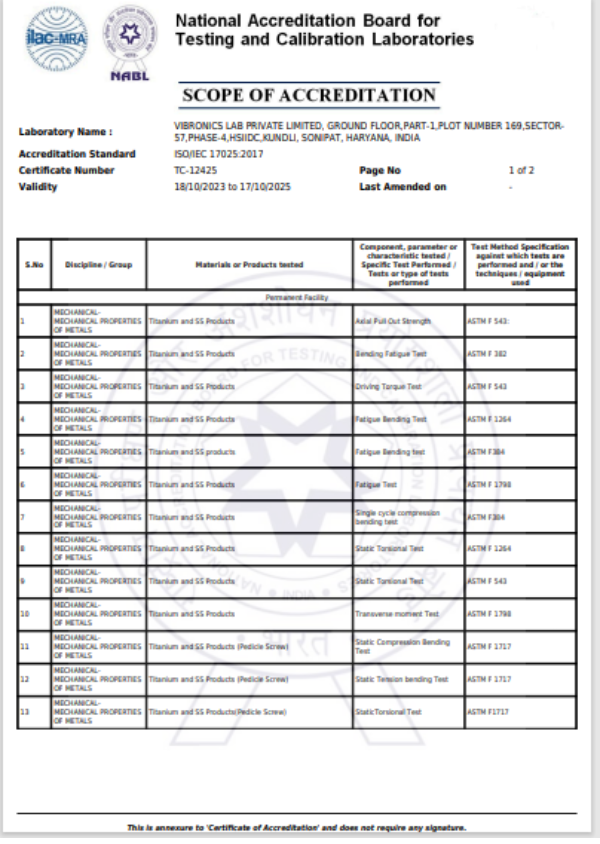
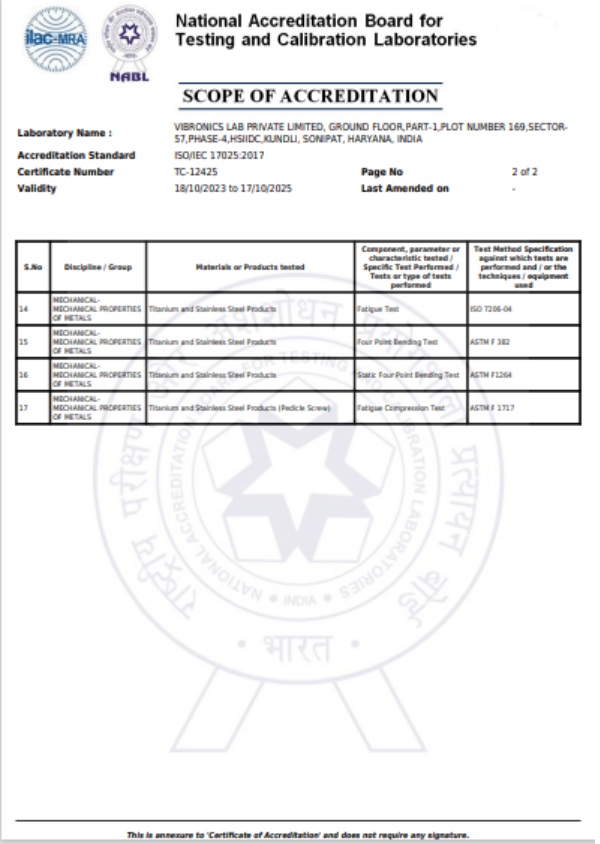
This test method covers a standard methodology by which to measure the attachment strength between the modular acetabular shell and liner. Although the methodology described does not replicate physiological loading conditions, it has been described as a means of comparing the integrity of various locking mechanisms
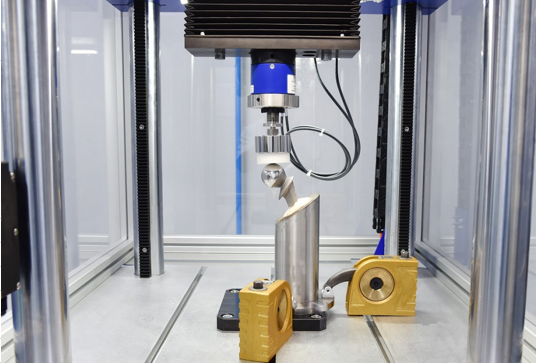
This part of ISO 7206 specifies a test method for determining the endurance properties of stemmed femoral components of total hip joint prostheses and stemmed femoral components used alone in partial hip joints under specified laboratory conditions. It also defines the conditions of testing so that the important parameters that affect the components are taken into account, and describes how the specimen is set up for testing.
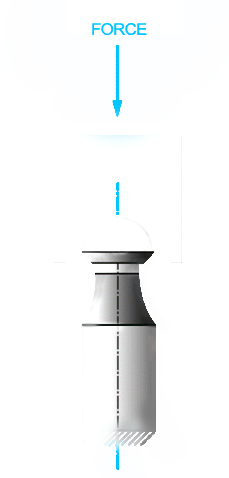
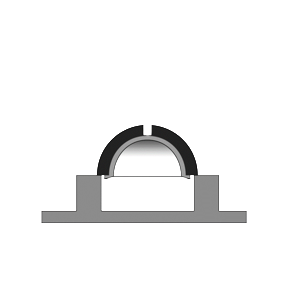
This testing method applies to components made of metallic and non-metallic materials, such as femoral heads of partial or total hip-joint replacements of modular construction (i.e. a head/neck conical taper connection).

This part of ISO 7206 describes a method of determining the torque required, under specified laboratory conditions, to loosen the fixation of the head of hip joint prostheses in which the head is not intended to rotate relative to the neck. It applies to the femoral component of total or partial hip joint replacements in which the head and neck/stem (in the following referred to as cone) are secured together by a locking conical taper or any other means and in which the head and cone are separate components, and which are made of metallic or non-metallic materials.

This specification provides requirements for materials, finish and marking, care and handling, and the acceptable dimensions and tolerances for metallic bone screws that are implanted into bone. The dimensions and tolerances in this specification are applicable only to metallic bone screws described in this specification.

This test method describes methods for single cycle bend testing in order to determine the intrinsic, structural properties of metallic bone plates. The test method measures the bending stiffness, bending structural stiffness, and bending strength of bone plates.
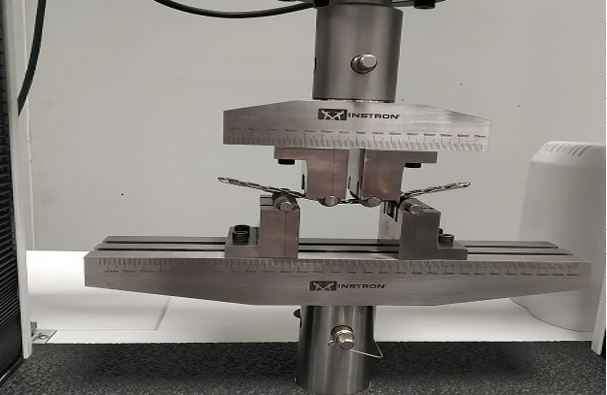
This test method covers the test procedure for performing cyclic bending fatigue testing of intramedullary fixation devices (IMFDs). The central part of the IMFD, with a straight and uniform cross section and away from screw holes or other interlocking features, is tested in cyclic four-point bending. This method may be used to determine the fatigue life at a specified maximum bending moment or to estimate the fatigue strength for a specified number of cycles.
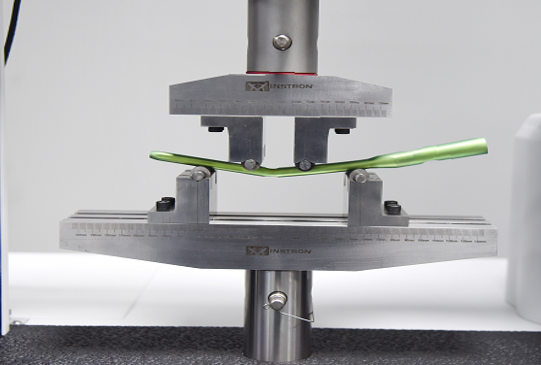
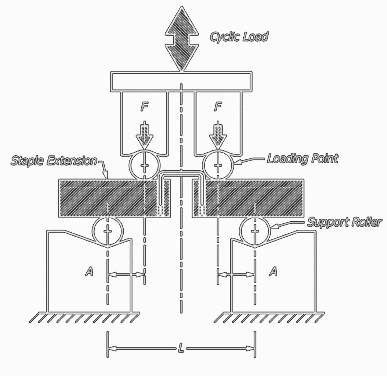
This test method covers procedures for the performance of constant amplitude fatigue testing of metallic staples used in internal fixation of the musculoskeletal system. This test method may be used when testing in air at ambient temperature or in an aqueous or physiological solution.
This test method provides a screening test for determining the amount of metal loss from plates and screws used for osteosynthesis (internal fixation of broken bones) due to fretting corrosion in the contact area between the screw head and the plate hole countersink area. The implants are used in the form they would be used clinically. The machine described generates a relative motion between plates and screws which simulates one type of motion pattern that can occur when these devices are used clinically.
This guide covers the measurement of uniaxial static and fatigue strength, and resistance to loosening of the component interconnection mechanisms of spinal arthrodesis implants.The purpose of this guide is to provide a means of mechanically characterizing different designs of spinal implant interconnections. Ultimately, the various components and interconnections should be combined for static and fatigue testing of the spinal implant construct. It is not the intention of this guide to address the analysis of spinal implant constructs or subconstructs or to define levels of performance of spinal implants as insufficient knowledge is available to predict the consequences of the use of particular spinal implant designs.

This test method describes methods for bending fatigue testing in order to determine intrinsic structural properties of metallic angled devices. The test method may be used to determine the fatigue life at a specific or over a range of maximum bending moment levels or to estimate the fatigue strength for a specified number of fatigue cycles of an angled device.
This test method covers the materials and methods for the static and dynamic testing of intervertebral body fusion device assemblies, spinal implants designed to promote arthrodesis at a given spinal motion segment.This test method is intended to provide a basis for the mechanical comparison among past, present, and future nonbiologic intervertebral body fusion device assemblies. This test method allows comparison of intervertebral body fusion device assemblies with different intended spinal locations and methods of application to the intradiscal spaces. This test method is intended to enable the user to compare intervertebral body fusion device assemblies mechanically and does not purport to provide performance standards for intervertebral body fusion device assemblies.

This specification provides a characterization of the design and mechanical function of external skeletal fixation devices (ESFDs), test methods for characterization of ESFD mechanical properties, and identifies needs for further development of test methods and performance criteria. The ultimate goal is to develop a specification, which defines performance criteria and methods for measurement of performance-related mechanical characteristics of ESFDs and their fixation to bone. It is not the intention of this specification to define levels of performance or case-specific clinical performance of the devices, as insufficient knowledge is available to predict the consequences of the use of any of these devices in individual patients for specific activities of daily living. Furthermore, it is not the intention of this specification to describe or specify specific designs for ESFDs.
This test method specifies the materials and methods for the axial compressive subsidence testing of non-biologic intervertebral body fusion devices, spinal implants designed to promote arthrodesis at a given spinal motion segment. This test method describes a static test method by specifying a load type and a specific method of applying this load. This test method is designed to allow for the comparative evaluation of intervertebral body fusion devices.

These test methods set out guidelines for load types and methods of applying loads. Methods for three static load types and one fatigue test are defined for the comparative evaluation of spinal implant assemblies.These test methods establish guidelines for measuring displacements, determining the yield load, and evaluating the stiffness and strength of the spinal implant assembly.

This test method establishes a standard methodology for determining the force required, under laboratory conditions, to disassemble tapers of implants that are otherwise not intended to release. Some examples are the femoral components of a total or partial hip replacement or shoulder in which the head and base component are secured together by a self-locking taper.