Knee constraint test ASTM F1223
Normative References
ASTM F1223: Standard Test Method for Determination of Total Knee Replacement Constraint
This test method covers the means by which a TKR constraint may be quantified according to motion delineated by the inherent articular design as determined while under specific loading conditions in an in vitro environment. Tests deemed applicable to the constraint determination are antero-posterior draw, medio-lateral shear, rotary laxity, valgus-varus rotation, and distraction, as applicable. Also covered is the identification of geometrical parameters of the contacting surfaces which would influence this motion and the means of reporting the test results.
In general, the medium (standard) size is tested. The tests are performed at room temperature while keeping the surfaces wet.



Dislocation mobile bearing ASTM F2724
Normative References
ASTM F2724: Standard Test Method for Evaluating Mobile Bearing Knee Dislocation.
This test protocol describes the test method to determine the relative safety threshold for mobile-bearing knee designs with respect to spin-out and spit-out of the tibial insert. A total of n=5 implants are tested at 0°, 60°, 90° and maximum flexion. The medial condyle is loaded with 80%, and the lateral condyle is loaded with 20% of the axial joint reaction force (100% = 710N). The femoral component is moved in ap-direction until luxation occurs.

Knee contact pressure test PI-17
Normative References
PI-17: Determination of Total Knee Implant Contact Pressure
ASTM F2083: Standard Specification for Knee Replacement Prosthesis
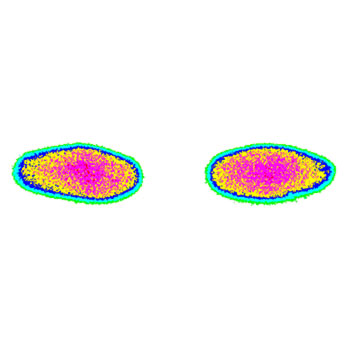
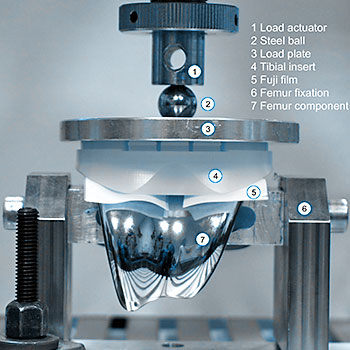
Pressure distribution and pressure level are two of the factors influencing wear of total knee replacements. Using pressure films, the contact area as well as the amount of pressure (in MPa) can be determined exactly. To gain reproducible results avoiding the disadvantages of pressure films, EndoLab® developed a computerized calibration method. An individual calibration is performed for every sheet and test series. Digital image processing is used to analyse the results.
The aim of the test is to evaluate the pressure distribution and total contact area between the femoral component and tibial insert, and between the femoral component and the patella insert of a total knee replacement system under different flexion angles and loads. These results can be used to develop optimized geometries.